A few times each year, Google makes updates to its search algorithm. Major updates like Panda and Penguin change everything we know—or think we know—about search engine optimization and the way our content ranks in search engine results pages (SERPs). Other updates, however, are smaller fine-tuning changes meant to adjust the functionality and user experience of Google search.
Google’s BERT update in late 2019 is one of the latter—though we could argue that it may have a slight impact on how we approach writing content for SEO over the next few years. Let’s dig a little deeper…
What Is BERT?
To understand what BERT is, you first need to understand the way search engines process language. So let’s back up for a moment (and get a little technical).
Have you ever wondered how search engines know what data to pull when you submit a search query? That’s thanks to artificial neural networks. These deep learning systems help machines recognize patterns so that they can retrieve information, provide answers to questions, and ultimately learn how to classify data.
One specific neural network model called Transformer has been found to be one of the most effective for natural language processing (i.e., how computers understand human language). What makes this model so unique is that, unlike other neural network models which process words in a phrase one by one in order, Transformer models process words in relation to all of the words within a phrase, thereby better understanding the context of the phrase, rather than just its pattern.
For search engines like Google, this model has been a game-changer, as it allows them to develop smarter algorithms for interacting with human language. And it was Google’s research into Transformer models that led them to the creation of BERT.
BERT—or Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers—is a natural language processing system derived from the Transformer model, and its introduction means Google can now view a string of words in a search query and understand the meaning behind them to deliver better results for its users.
How Does BERT Affect Google Search?
After initial launch in October 2019 for English language queries—followed by a rollout for 70 additional languages in December 2019—Google is now fully utilizing BERT in search. It’s believed that this update will impact 1 in 10 of all searches. If you’re a content marketer or an SEO strategist, this might give you pause. But Google says there’s no reason to worry about your search engine rank, as the update is more focused on helping Google users.
BERT, like all Google algorithm updates, is intended to improve the search engine experience for users by providing them with the most relevant results. It’s comparable to Google’s RankBrain update from 2015, in which the search engine utilized an interpretation model that took patterns like searcher location and behavior to determine user intent for delivering the best results. Of course, BERT is more advanced than that.
By giving its search algorithm the ability to comprehend phrases semantically, Google is more likely to interpret nuance in longer conversational queries, especially in instances where prepositions like “to” and “for” can drastically change the meaning of a phrase.
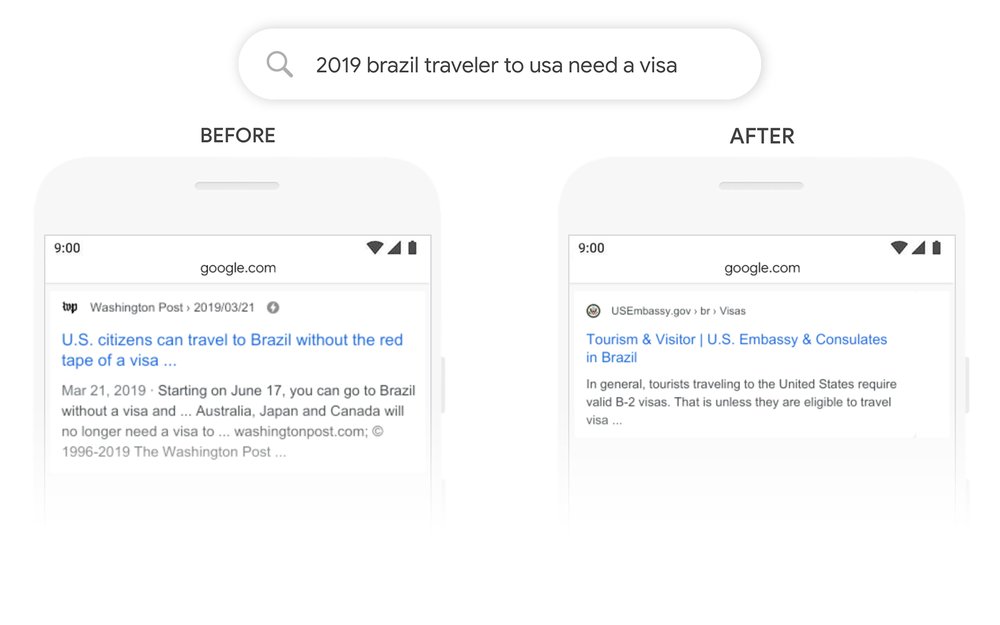
In the above example provided by Google, you can see how BERT could affect the results that show for a question that’s implied. The phrase “2019 brazil traveler to usa need a visa” is a complex search query essentially asking the question “Do I need a visa when traveling from Brazil to the USA in 2019?” It combines three crucial pieces that show Google what it needs to know about who the searcher is and what they’re looking for. Let’s break it down…
- 2019: Including the year tells Google that the searcher wants to receive the most up-to-date information regarding their query.
- Brazil Traveler to USA: The use of “to” tells Google that the searcher is from Brazil and looking for information about traveling to the USA, not the other way around.
- Need a Visa: This key phrase tells Google what the searcher is ultimately after.
Prior to BERT, Google would have looked at “2019 brazil traveler to usa need a visa” and recognized important words like USA, Brazil, Traveler, and Visa, pulling out results it believed to be the most relevant because they contained those exact words—and the searcher would get results that were technically relevant, but not useful in answering their implied question. With BERT, the search engine is now able to recognize the context of all words in the query and, more importantly, understand how important the “to” is in relation to the words Brazil and USA.
Now, neural network researchers and SEO experts alike have come out and said that BERT’s abilities shouldn’t be overhyped. In fact, one natural language processing researcher Allyson Ettinger pointed out that BERT still struggles with elementary aspects of human language like negation. But even though artificial intelligence has a long way to go when it comes to truly understanding human language, BERT is still pretty impressive.
And the more Google gets better at translating user intent from billions of language variations, the more our content marketing and SEO work could potentially change as well.
Will BERT Impact SEO Content Writing?
Naturally, the first thing on every digital marketer’s mind when Google releases an algorithm update is “How is this going to affect my search engine optimization efforts?” With BERT, Google has made it abundantly clear that marketers do not need to make any adjustments to their SEO strategies. Google public search liaison Danny Sullivan even took to Twitter to recommend that marketers continue focusing on providing great content.
There’s nothing to optimize for with BERT, nor anything for anyone to be rethinking. The fundamentals of us seeking to reward great content remain unchanged.
— Danny Sullivan (@dannysullivan) October 28, 2019
While everything Google has said about BERT essentially boils down to “Hey, don’t think there’s a marketing tactic you can take advantage of here to rank higher in our results,” to say BERT will have no effect on SEO efforts whatsoever seems a bit unfair. For one, this update does have an impact on featured snippets, which means marketers could see changes in Google featured snippet placement with their content. Moreover, search engines getting better at understanding searcher language through a contextual lens plays a role in how we approach the creation of what Sullivan refers to as “great content.”
After all, language is at the core of content marketing and SEO. When we write marketing copy and optimize our websites for search engine results, we research the language searchers use. We look at how they phrase their questions and which words they choose when they search for products, services, or answers. We’re constantly tailoring our language to searchers—the same way Google is tailoring its algorithm to its users.
There’s not a direct one-to-one connection between Google implementing BERT and marketers seeing changes to their SEO. But that doesn’t mean BERT isn’t important for us to understand. If anything, this algorithm update is a reminder for content marketers of how people use Google search—how even the smallest inclusion of a preposition like “to” in a search phrase can hold so much semantic weight.
Similar to how we’re evaluating our sentence structures and word choice for voice search optimization, we need to think about the larger possibilities that might arise for content marketing with BERT and its language processing iterations.
Looking for help with your brand’s content marketing and SEO? Hurrdat offers SEO content writing services, including webpage optimization, blogging, product descriptions, and more. Contact us today!